ESA Space Science News
|
The European Space Agency (ESA)
is Europe’s gateway to space. Its mission is to shape the development of Europe’s space capability and ensure that investment in space continues to deliver benefits to the citizens of Europe and the world. |
|||||||||||||||||
|







 Feed
Feed Scan with QR Code Reader
Scan with QR Code Reader mobi
mobi





 Video:
00:06:44
Video:
00:06:44

 Image:
From pebbles to planets
Image:
From pebbles to planets 

 Image:
Webb wows with incredible detail in star-forming system
Image:
Webb wows with incredible detail in star-forming system
 Image:
Webb visits a star-forming spiral
Image:
Webb visits a star-forming spiral Image:
Celebrating Solar Orbiter and the women behind the mission
Image:
Celebrating Solar Orbiter and the women behind the mission  Image:
XMM-Newton finds two stray supernova remnants
Image:
XMM-Newton finds two stray supernova remnants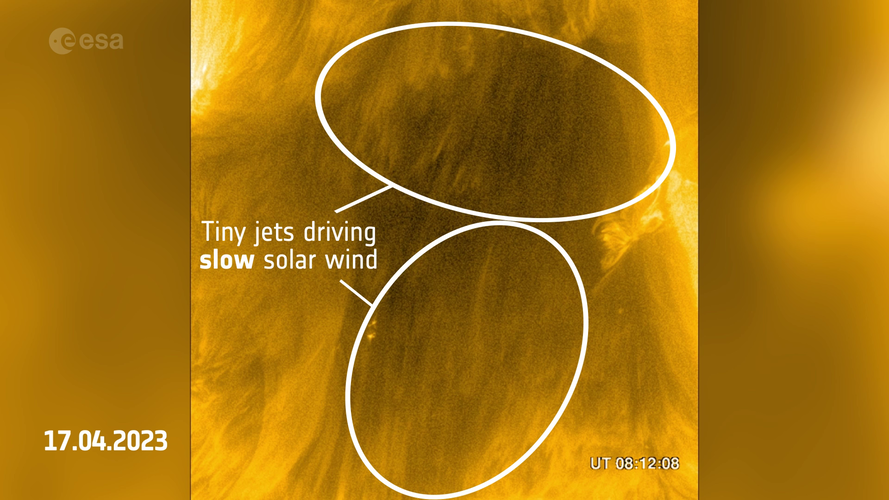 Video:
00:00:40
Video:
00:00:40
 Video:
00:01:40
Video:
00:01:40
 Video:
00:01:20
Video:
00:01:20
 Video:
00:02:05
Video:
00:02:05