Near Earth Objects
| |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| des | cd | dist | v_rel | h * | |
| 2025 FN2 | 2025-Mar-25 04:02 | 0.024589 | 11.790342 | 25.77 | |
| 2022 ER6 | 2025-Mar-25 06:36 | 0.098576 | 9.946951 | 22.91 | |
| 2025 FT | 2025-Mar-25 08:52 | 0.013047 | 8.992596 | 27.206 | |
| 2019 SP2 | 2025-Mar-25 18:01 | 0.083374 | 8.193540 | 24.02 | |
| 152754 | 2025-Mar-25 19:30 | 0.122247 | 11.380009 | 19.31 | |
| 2025 FK2 | 2025-Mar-25 22:20 | 0.030327 | 3.506643 | 27.041 | |
| 2025 FR2 | 2025-Mar-26 01:44 | 0.018153 | 10.533340 | 26.731 | |
| 2014 TN17 | 2025-Mar-26 11:34 | 0.034040 | 21.467192 | 21.55 | |
| 2025 FT2 | 2025-Mar-26 18:59 | 0.132020 | 14.537828 | 23.361 | |
| 2025 FD2 | 2025-Mar-26 19:20 | 0.014093 | 8.943080 | 27.477 | |
| 2025 FS5 | 2025-Mar-26 22:09 | 0.049279 | 21.107883 | 24.194 | |
| 2025 DW5 | 2025-Mar-26 22:21 | 0.042312 | 5.638194 | 24.68 | |
| 2007 EJ88 | 2025-Mar-27 06:28 | 0.048561 | 25.851252 | 23.4 | |
| 2025 FC4 | 2025-Mar-27 07:59 | 0.028778 | 11.388673 | 25.771 | |
| 2025 DV22 | 2025-Mar-27 12:09 | 0.042352 | 12.221574 | 23.956 | |
| 2025 FO6 | 2025-Mar-27 13:43 | 0.005404 | 12.526912 | 27.493 | |
| 2024 GE3 | 2025-Mar-27 14:17 | 0.165942 | 4.979092 | 26.08 | |
| 2016 ED157 | 2025-Mar-27 21:08 | 0.116614 | 2.499493 | 24.65 | |
| 2025 DU3 | 2025-Mar-28 00:05 | 0.131040 | 13.367778 | 22.393 | |
| 2023 XW1 | 2025-Mar-28 08:01 | 0.170977 | 9.371803 | 27.51 | |
| Data Courtesy of CNEOS | |||||
| |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| des | cd | dist | v_rel | h * | |
| 2025 FX2 | 2025-Mar-24 15:49 | 0.001832 | 25.093799 | 27.348 | |
| 2025 FS | 2025-Mar-24 09:55 | 0.007813 | 13.651737 | 26.021 | |
| 2025 FQ2 | 2025-Mar-24 08:25 | 0.018188 | 6.865491 | 27.778 | |
| 2025 FK3 | 2025-Mar-24 08:03 | 0.000816 | 20.547756 | 29.092 | |
| 2025 FC2 | 2025-Mar-23 22:11 | 0.001690 | 13.418673 | 28.394 | |
| 2025 FY1 | 2025-Mar-23 21:23 | 0.004512 | 14.322984 | 26.89 | |
| 2025 DA15 | 2025-Mar-23 15:55 | 0.043331 | 7.757370 | 24.976 | |
| 2025 FZ | 2025-Mar-22 23:38 | 0.008480 | 7.154572 | 27.593 | |
| 2025 FB2 | 2025-Mar-22 06:53 | 0.020860 | 13.158967 | 26.622 | |
| 2021 FH1 | 2025-Mar-21 13:31 | 0.009955 | 13.840552 | 25.28 | |
| 2025 FA2 | 2025-Mar-21 13:08 | 0.014358 | 9.820249 | 26.947 | |
| 2025 FJ | 2025-Mar-21 06:35 | 0.006243 | 10.969776 | 27.965 | |
| 2025 FE | 2025-Mar-21 02:02 | 0.020207 | 15.015812 | 24.706 | |
| 2025 FG | 2025-Mar-20 20:45 | 0.018584 | 5.497326 | 27.282 | |
| 2025 FS2 | 2025-Mar-20 20:09 | 0.002749 | 13.057899 | 28.08 | |
| 2025 FL | 2025-Mar-20 19:44 | 0.003089 | 8.970754 | 26.407 | |
| 2025 FF | 2025-Mar-20 15:49 | 0.026382 | 6.288206 | 26.613 | |
| 2025 FC1 | 2025-Mar-19 23:26 | 0.004279 | 18.756712 | 27.642 | |
| 2025 EQ2 | 2025-Mar-19 19:10 | 0.013431 | 6.180010 | 26.906 | |
| 2025 FO2 | 2025-Mar-19 15:52 | 0.008763 | 12.776913 | 27.878 | |
| 2025 FQ4 | 2025-Mar-19 12:37 | 0.018285 | 14.488727 | 22.916 | |
| 2025 FQ5 | 2025-Mar-19 04:18 | 0.005109 | 4.865451 | 26.812 | |
| 2025 FF2 | 2025-Mar-19 03:47 | 0.009023 | 20.734027 | 27.116 | |
| 2025 FD1 | 2025-Mar-19 01:01 | 0.006772 | 23.747545 | 27.329 | |
| 2025 FA1 | 2025-Mar-18 19:00 | 0.015473 | 11.444205 | 26.093 | |
| 2025 FS6 | 2025-Mar-18 17:57 | 0.007347 | 7.654649 | 27.044 | |
| 2025 FC | 2025-Mar-18 15:42 | 0.000442 | 17.175316 | 28.792 | |
| 2025 DU25 | 2025-Mar-18 12:41 | 0.007452 | 5.337336 | 27.25 | |
| 2025 FP | 2025-Mar-18 10:59 | 0.005251 | 8.905594 | 27.22 | |
| 2025 FD | 2025-Mar-18 04:26 | 0.013002 | 24.551796 | 23.835 | |
| 2025 FN | 2025-Mar-17 18:10 | 0.014704 | 13.262104 | 27.691 | |
| 2025 EC1 | 2025-Mar-16 19:28 | 0.021946 | 6.495683 | 26.339 | |
| 2025 FO | 2025-Mar-15 21:04 | 0.015212 | 18.044114 | 23.846 | |
| 2025 DO27 | 2025-Mar-15 18:45 | 0.044069 | 15.233276 | 24.788 | |
| 2020 FO | 2025-Mar-15 13:47 | 0.034233 | 20.581934 | 25.9 | |
| 2025 EF4 | 2025-Mar-15 09:53 | 0.003067 | 5.853212 | 24.662 | |
| 2025 DV4 | 2025-Mar-15 06:42 | 0.046080 | 6.986095 | 25.472 | |
| 2025 EG2 | 2025-Mar-15 00:09 | 0.049763 | 11.586513 | 24.636 | |
| Data Courtesy of CNEOS | |||||
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| des | cd | dist | v_rel | h * |
| 2020 VT4 | 2020-Nov-13 17:21 | 4.50910597356063e-05 | 13.427119549171 | 28.61 |
| 2024 XA | 2024-Dec-01 09:46 | 5.16452821681997e-05 | 13.565976367738 | 31.64 |
| 2024 LH1 | 2024-Jun-06 14:02 | 5.41335085929206e-05 | 17.404073125193 | 30.79 |
| 2024 UG9 | 2024-Oct-30 12:42 | 5.91577148660634e-05 | 20.304681007654 | 32.61 |
| 2020 QG | 2020-Aug-16 04:09 | 6.22797984976286e-05 | 12.330867306387 | 29.90 |
| 2021 UA1 | 2021-Oct-25 03:07 | 6.30135027524984e-05 | 15.835006860335 | 31.84 |
| 2025 BP6 | 2025-Jan-26 01:10 | 6.49203901827142e-05 | 21.046976456134 | 31.82 |
| 2023 BU | 2023-Jan-27 00:29 | 6.66251002445381e-05 | 9.267245151395 | 29.69 |
| 2023 RS | 2023-Sep-07 14:26 | 6.92592750346214e-05 | 13.588128222566 | 32.32 |
| 2011 CQ1 | 2011-Feb-04 19:39 | 7.92234674587619e-05 | 9.693440511087 | 32.1 |
| Data Courtesy of CNEOS | Since 1st Jan 2000 | |||
Key
des - primary designation of the asteroid or comet
cd - time of close-approeach (formatted calendar date/time)
dist - nominal approach distance (au)
v_rel - velocity relative to the approach body at close approach (km/s)
h - absolute magnitude H (mag)
* - An asteroid's absolute magnitude is the visual magnitude an observer would record if the asteroid were placed 1 Astronomical
Unit (AU) away, and 1 AU from the Sun and at a zero phase angle.
1 AU = Astronomical Unit is approximately the mean distance between the Earth and the Sun, ~150 million kilometers
1 LD = Lunar Distance = ~384,000 kilometers
| Near-Earth Objects – The Watchers |
|---|
Watching the world evolve and transform |
| February 25th, 2025 13:09:11 EST -0500 Impact probability for asteroid 2024 YR4 drops to 0.0017%, moon impact at 1.7% Asteroid 2024 YR4's impact risk has dropped to 0.0017%, placing it a level 0 on the Torino Impact Hazard Scale. There remains a 1.7% chance of the asteroid impacting the moon on December 22, 2032. |
| February 21st, 2025 09:44:16 EST -0500 Asteroid 2024 YR4’s impact probablity drops to 0.16% Asteroid 2024 YR4 is making headlines again after new calculations revealed that the asteroid now has an impact probability to Earth of just 0.16% in 2032. |
| February 18th, 2025 14:25:21 EST -0500 Asteroid 2024 YR4 now has a 1 in 38 chance of impact in 2032 The impact risk of asteroid 2024 YR4 in 2032 increased from 1.8% to 2.6% (1 in 38) with new trajectory simulations and refined calculations. While the increase remains within a low-risk range, continued monitoring and additional observations will be necessary to further refine impact predictions. |
| February 6th, 2025 14:40:51 EST -0500 Asteroid 2024 YR4 impact risk updated to 1.8% The impact risk of asteroid 2024 YR4 in 2032 increased from 1.2% to 1.8% on February 6, 2025, following new trajectory simulations and refined calculations. While the increase remains within a low-risk range, continued monitoring and additional observations will be necessary to further refine impact predictions. |
| February 3rd, 2025 12:57:02 EST -0500 Asteroid 2024 YR4 triggers planetary defense procedures A newly discovered asteroid designated 2024 YR4 has activated global planetary defense protocols after initial observations indicated a small but notable chance of impact in seven years. International monitoring networks have begun refining its trajectory, while space agencies evaluate potential response strategies, including possible deflection measures. |
| CNEOS Recent News |
|---|
Recent news stories from the Center for Near-Earth Object Studies (CNEOS) |
February 24th, 2025 03:00:00 EST -0500 Latest Calculations Conclude Asteroid 2024 YR4 Now Poses No Significant Threat to Earth in 2032 and Beyond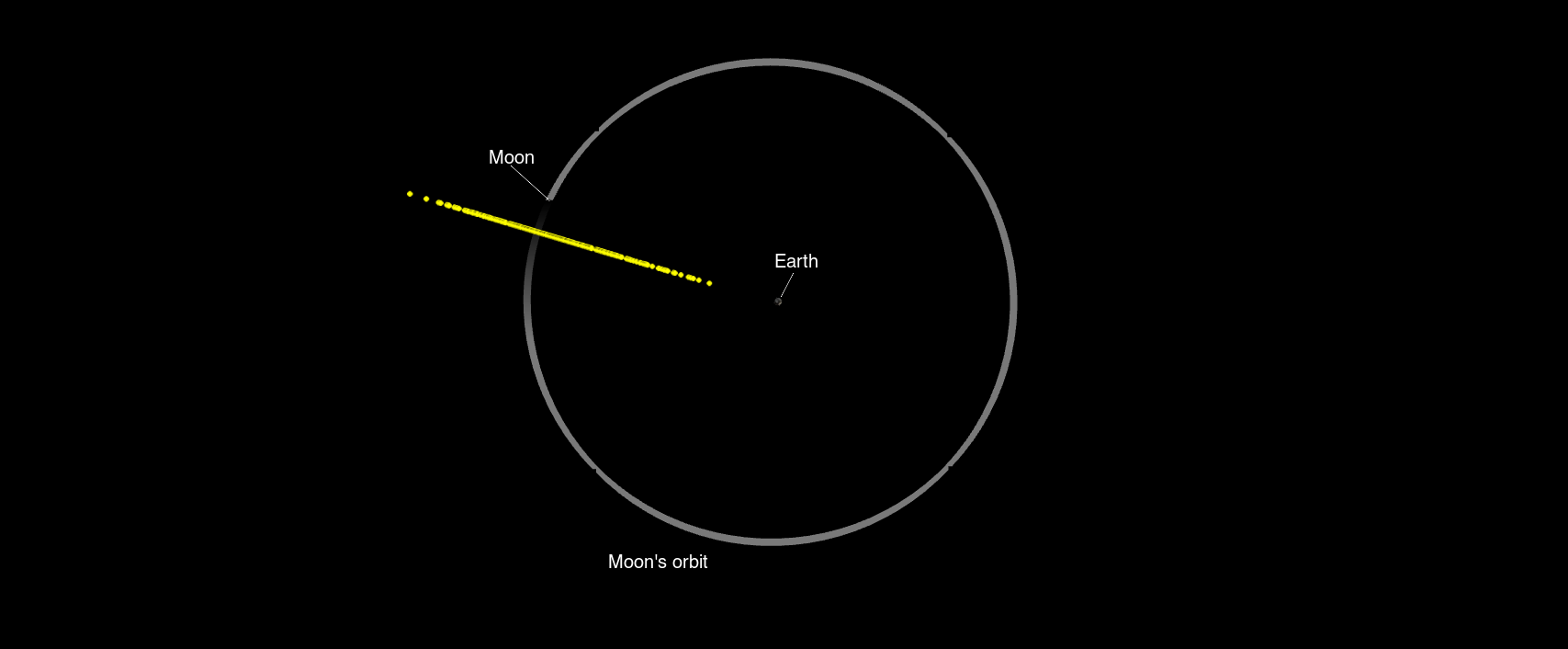
NASA has significantly lowered the risk of near-Earth asteroid 2024 YR4 as an impact threat to Earth for the foreseeable future. |
January 31st, 2025 03:00:00 EST -0500 Asteroid 2024 YR4 reaches level 3 on the Torino Scale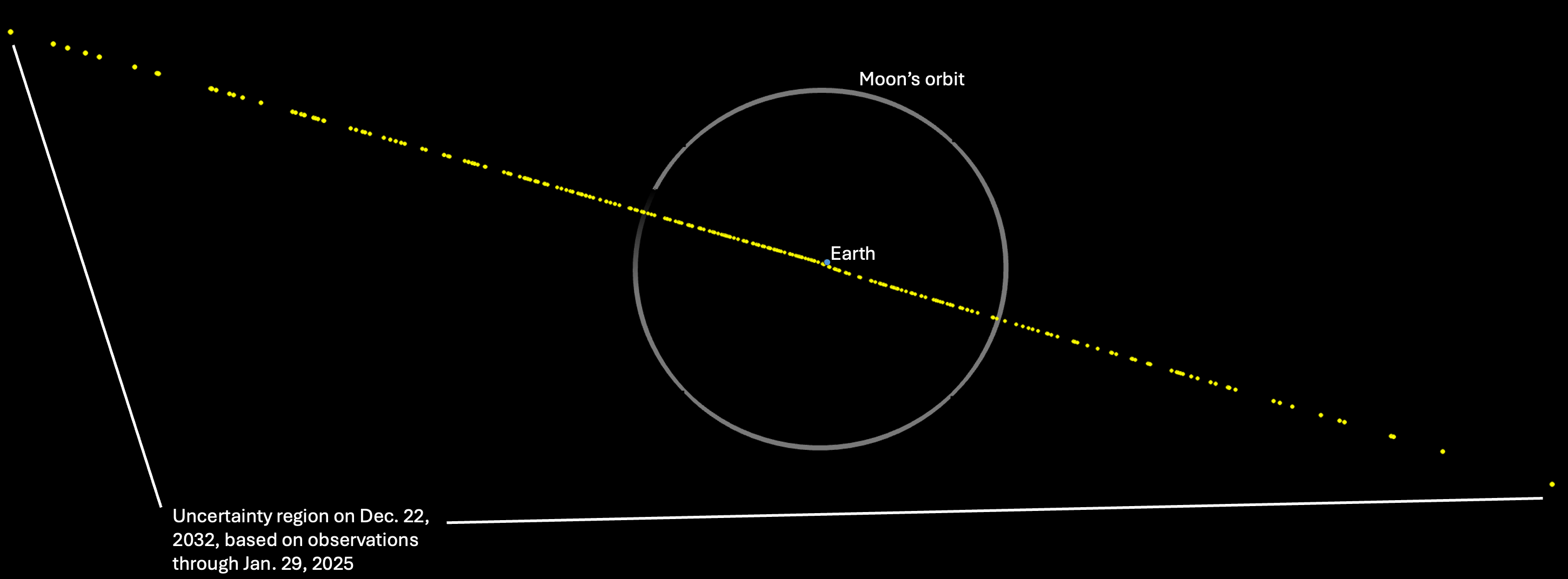
NASA analysis of a near-Earth asteroid, designated 2024 YR4, indicates it has a small chance of impacting Earth on Dec. 22, 2032. |
March 19th, 2024 03:00:00 EDT -0400 NASA Study: Asteroid’s Orbit, Shape Changed After DART Impact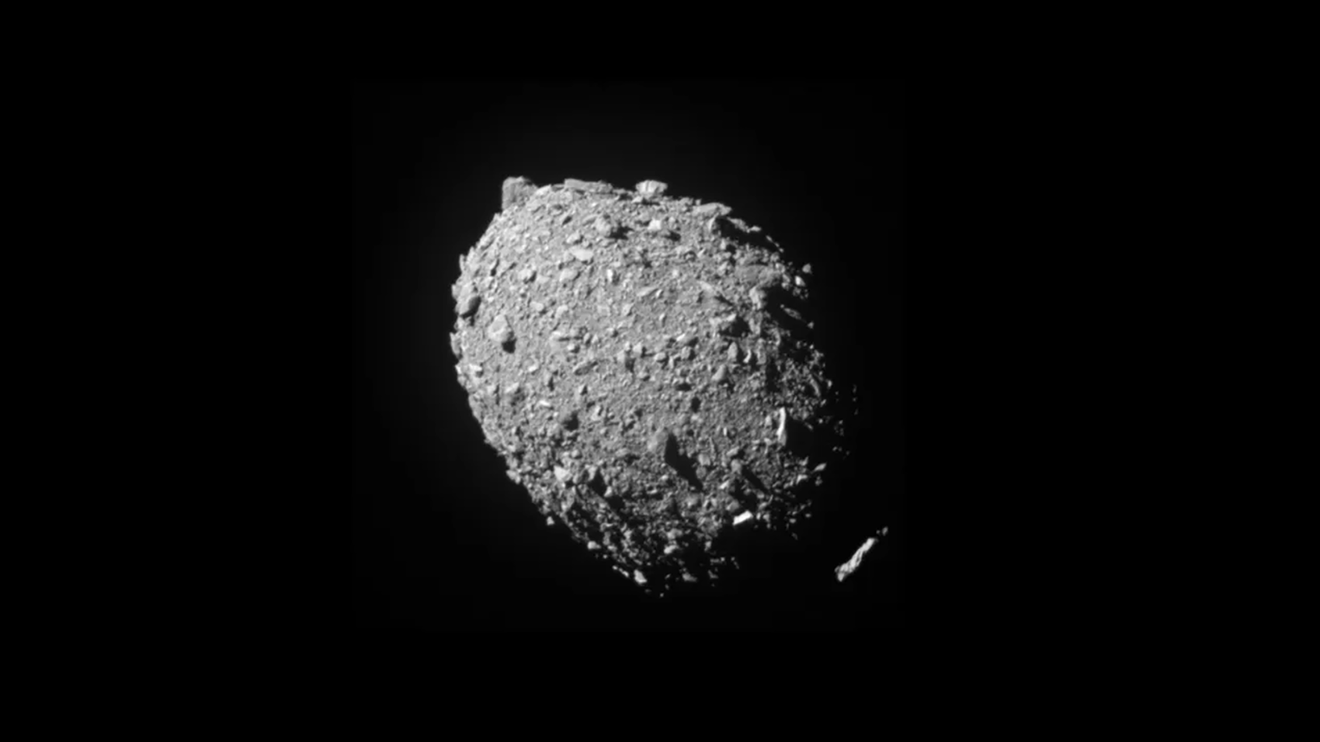
After NASA’s historic Double Asteroid Redirection Test, a JPL-led study has shown that the shape of asteroid Dimorphos has changed and its orbit has shrunk. |
January 24th, 2024 03:00:00 EST -0500 NASA System Predicts Impact of a Very Small Asteroid Over Germany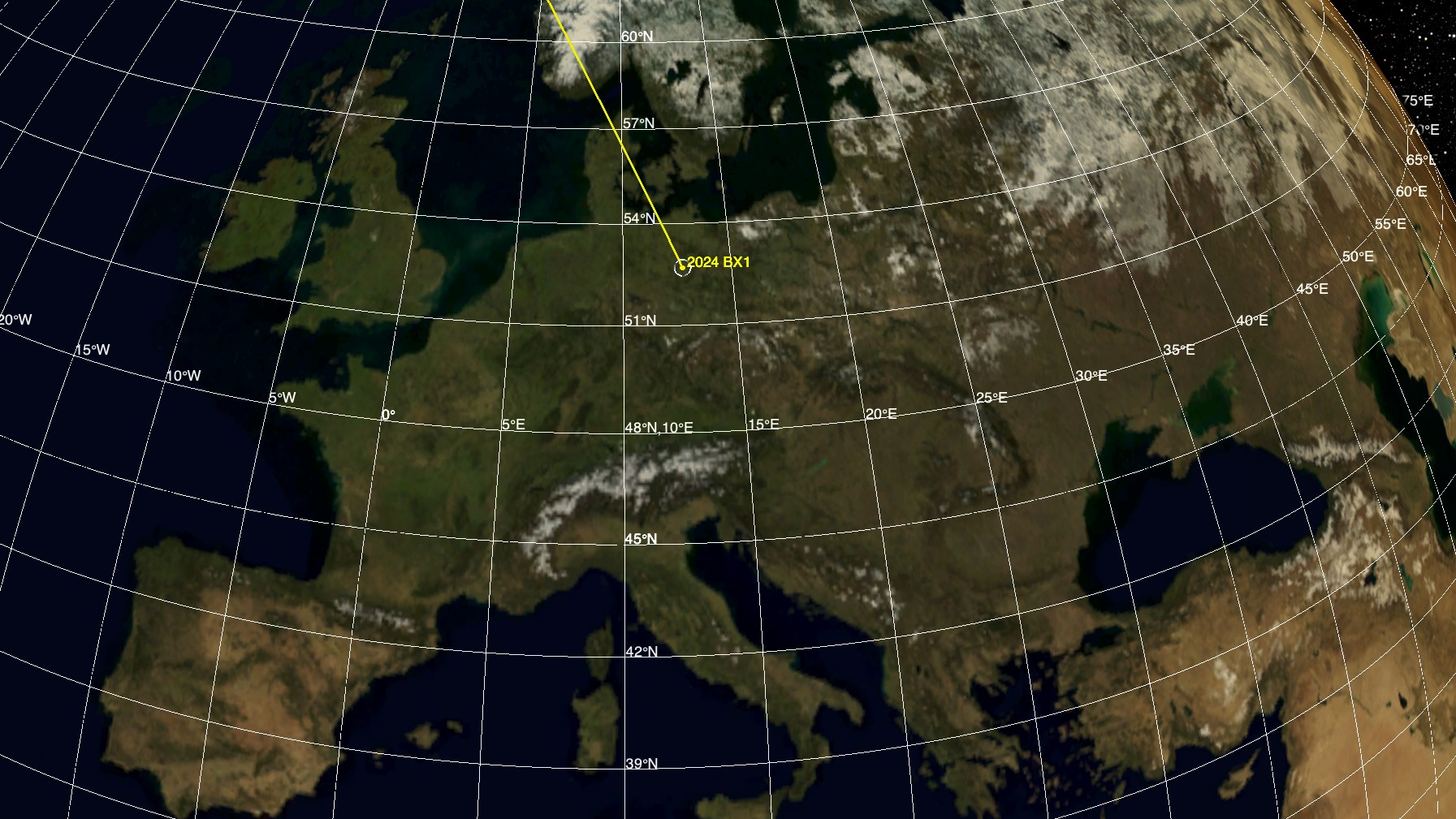
The Scout impact assessment system calculated where and when the asteroid 2024 BX1 would impact Earth’s atmosphere, providing a useful demonstration of planetary defense capability. |
February 14th, 2023 03:00:00 EST -0500 CNEOS Predicts Another Small Asteroid Impact, This One over Northwestern France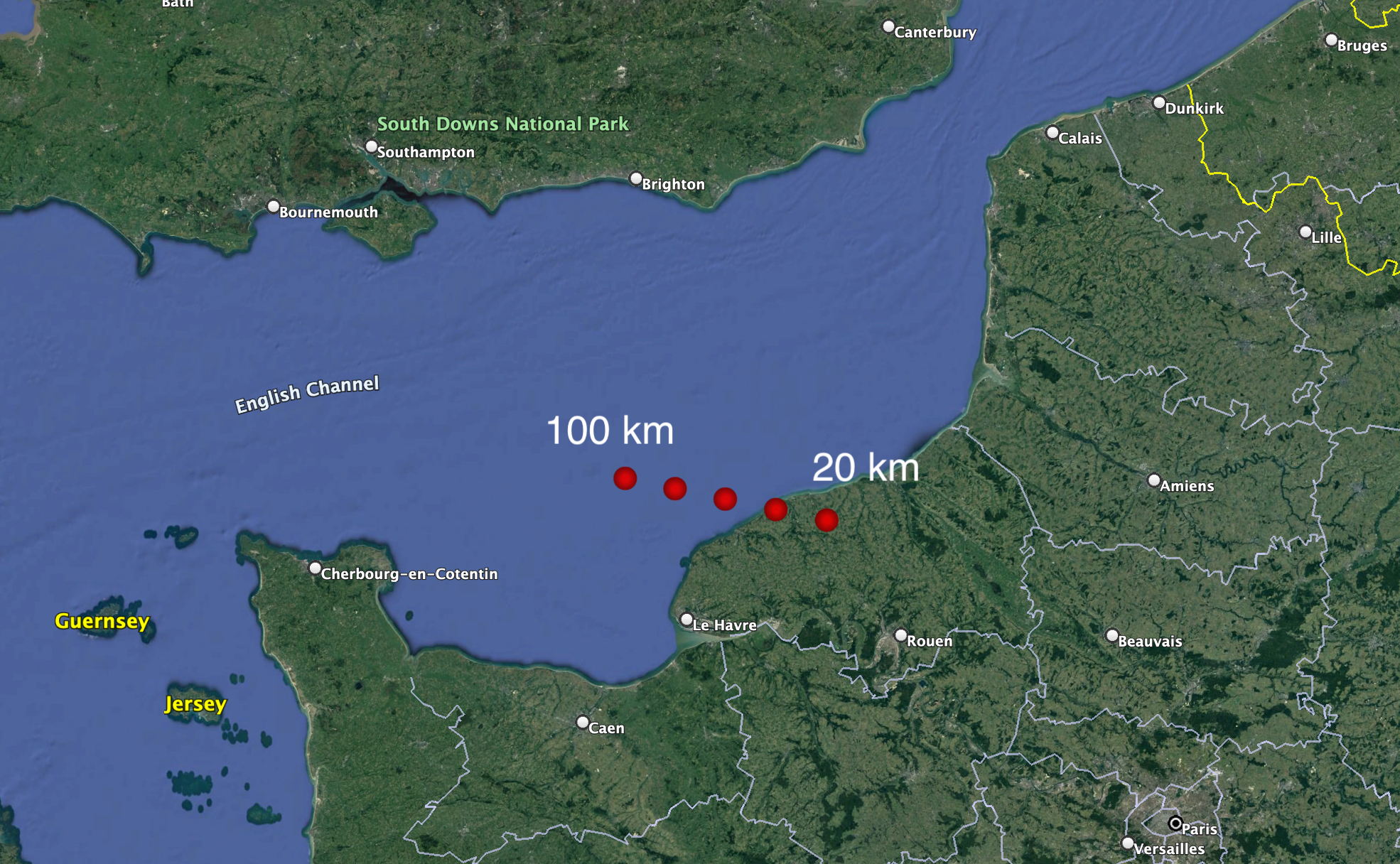
Another tiny asteroid on a collision course with Earth was detected over the weekend, and JPL’s CNEOS Scout system accurately predicted where and when the impact would happen, well before it actually occurred. |
Near Earth Objects |
|
Near-Earth Objects (NEOs) are comets and asteroids that have been nudged by the
gravitational attraction of nearby planets into orbits that allow them to enter
the Earth's neighborhood. Composed mostly of water ice with embedded dust particles,
comets originally formed in the cold outer planetary system while most of the rocky
asteroids formed in the warmer inner solar system between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.
The scientific interest in comets and asteroids is due largely to their status as the relatively unchanged remnant debris from the solar system formation process some 4.6 billion years ago. The giant outer planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune) formed from an agglomeration of billions of comets and the left over bits and pieces from this formation process are the comets we see today. Likewise, today's asteroids are the bits and pieces left over from the initial agglomeration of the inner planets that include Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars |
|
|
| The vast majority of NEOs are asteroids, referred to as Near-Earth Asteroids (NEAs). NEAs are divided into groups (Aten, Apollo, Amor) according to their perihelion distance (q), aphelion distance (Q) and their semi-major axes (a). See table |
| Group | Description | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| NECs | Near-Earth Comets | q<1.3 AU, P<200 years |
| NEAs | Near-Earth Asteroids | q<1.3 AU |
| Atiras | NEAs whose orbits are contained entirely with the orbit of the Earth (named after asteroid 163693 Atira). |
a<1.0 AU, Q<0.983 AU |
| Atens | Earth-crossing NEAs with semi-major axes smaller than Earth's (named after asteroid 2062 Aten). |
a<1.0 AU, Q>0.983 AU |
| Apollos | Earth-crossing NEAs with semi-major axes larger than Earth's (named after asteroid 1862 Apollo). |
a>1.0 AU, q<1.017 AU |
| Amors | Earth-approaching NEAs with orbits exterior to Earth's but interior
to Mars' (named after asteroid 1221 Amor). |
a>1.0 AU, 1.017<q<1.3 AU |
| PHAs | Potentially Hazardous Asteriods: NEAs whose
Minimum Orbit Intersection Distance (MOID) with the Earth is 0.05 AU or less and whose absolute magnitude (H) is 22.0 or brighter. |
MOID<=0.05 AU, H<=22.0 |
NEO - RECENT CLOSE APPROACHES TO EARTH |
| Near Earth Objects - Our solar system is teeming with asteroids and comets, some of which periodically pass close to Earth. These space rocks, called near-Earth objects, provide good opportunities for study and can also be potentially dangerous to Earth. Ask the dinosaurs !!! |
|
April 28th 2020 ASTEROID NEAR MISS: A newly-discovered asteroid designated 2020 HS7 will flyby Earth at a very close distance of 0.11 LD / 0.00029 AU (43 383 km / 26 957 miles) at 18:51 UTC on April 28, 2020. |
|
September 1st 2018 ASTEROID NEAR MISS: Asteroid named 'Florence' and is about 2.7 miles in length NASA has warned that the largest Earth-bound asteroid ever seen by NASA Florence will fly by at a relatively safe distance of 4.4 million miles away, around 18 times the distance between the Earth and the moon, but still close enough to be classed as a near-Earth object. It will be visible in small telescopes for several nights as it moves through the constellations Piscis Austrinus, Capricornus, Aquarius and Delphinus. |
|
October 12th 2017 ASTEROID NEAR MISS: 2012 TC4 The large space rock, named 2012 TC4, was first spotted five years ago by the Pan-STARRS telescope at the Haleakala Observatory, in Hawaii, before disappearing as it orbits the sun. It then reemerged in July on a trajectory well inside our lunar orbit. Scientists said the asteroid swung by Earth about 6:42am BST, 42,000 kilometers) above Antarctica at 0542 GMT Thursday. That's about 11 percent the distance between Earth and the moon, and just beyond the orbit of geostationary satellites.. |
|
September 1st 2017 ASTEROID NEAR MISS: At 1206 GMT, the roughly 2.7-mile-wide (4.4 kilometers) asteroid 3122 Florence came within a mere 4.4 million miles (7 million km) of Earth � just 18 times the distance from our planet to the moon. |
|
April 19th 2017 ASTEROID NEAR MISS: According to NASA, the asteroid 2014 JO25 will come within 4.6 lunar distances, This will be the closest of an asteroid of this size since a September 2004, with an estimated diameter of 0.65 km, larger than the Rock of Gibraltar. |
|
February 2nd 2017 ASTEROID NEAR MISS: A newly discovered asteroid 2017 BS32 will flyby Earth on February 2, 2017 at a distance of 0.41 LD from the surface. This near-Earth object belongs to Aten group of asteroids. 2017 BS32 was discovered on January 30 by Pan-STARRS 1, Haleakala. Its estimated size is between 11 and 25 m (36 to 82 feet). It will flyby Earth at 20:27 UTC on February 2 at a distance of 0.41 LD (161 280 km / 100 214 miles) from the surface at a speed (relative to Earth) of 11.56 km/s. This is the fourth know near-Earth asteroid to pass very close to Earth (below 1 LD) since January 8, 2017 |
|
January 26th 2015 ASTEROID NEAR MISS: The asteroid 2004 BL86 will fly by Earth on Jan. 26, passing at a range of about 745,000 miles (1.2 million kilometers), about three times the distance between the Earth and the moon. It will be the asteroid's closest approach to Earth for the next 200 years, according to NASA scientists. Asteroid 2004 BL86 is nearly 1,800 feet (549 meters) in diameter, but there is no risk of it hitting the Earth when it zips by. The next asteroid of similar size to come near Earth will be the asteroid 1999 AN10, which will make its closest approach in 2027, according to the NASA statement |
|
February 18th 2014 ASTEROID NEAR MISS: Asteroid 2000 EM26. A "potentially hazardous" asteroid the size of three football fields will come uncomfortably close to Earth early on Tuesday. The space rock, known as 2000 EM26, poses no threat and will pass the Earth at just under nine times the distance to the moon. But it is defined as a potentially hazardous near-Earth object (NEO) large enough to cause significant damage in the event of an impact. Scientists estimate the asteroid, travelling at 27,000mph, is 270 metres (885ft) wide. At its closest approach at 2am UK time, the rock will be 2.1m miles from Earth, or 8.8 lunar distances. |
|
February 15th 2013 ASTEROID NEAR MISS: Asteroid 2012 DA14 will be closest to Earth on February 15, 2013 at about 19:24 GMT (2:24 p.m. EST or 11:24 a.m. PST), when it will be at a distance of about 27,700 kilometers (17,200 miles) above the Earth's surface. This is so close that the asteroid will actually pass inside the ring of geosynchronous satellites, which is located about 35,800 kilometers (22,200 miles) above the equator, but still well above the vast majority of satellites, including the International Space Station. At its closest, the asteroid will be only about 1/13th of the distance to the Moon. The asteroid will fly by our planet quite rapidly, at a speed of about 7.8 kilometers/second (17,400 miles/hour) in a south-to-north direction with respect to the Earth 15/2/2013 03:20 GMT In a seperate incident a meteor crashing in Russia's Ural mountains has injured at least 950 people, as the shockwave blew out windows and rocked buildings. Many videos have appeared on the internet |
|
January 27th 2012 ASTEROID NEAR MISS: 2012 BX34 is a small Aten asteroid that made a close flyby of the Earth on 27 January 2012. The asteroid passed within 0.0004371 AU (65,390 km; 40,630 mi) of Earth during its closest approach at 15:25 GMT, conducting one of the closest asteroid passes on record. 2012 BX34 measures around 8 meters (26 ft) across; if it had impacted in 2012, it would have been too small to pass through Earth's atmosphere intact. |
|
November 8th 2011 ASTEROID NEAR MISS: Near-Earth asteroid 2005 YU55 passed within 0.85 lunar distances from the Earth. This was the closest an asteroid has been to Earth in 200 years, according to Nasa. It is also the largest space rock fly-by Earth has seen since 1976; the next visit by a large asteroid will be 2028. The aircraft-carrier-sized asteroid was darkly coloured in visible wavelengths and nearly spherical, lazily spinning about once every 20 hours as it raced through our neighbourhood of the Solar System. |
| January 13 2010 ASTEROID NEAR MISS: at 12:46 pm Greenwich time Asteroid 2010 AL30, will make a close approach to the Earth's surface to within 76,000 miles, about 10-15 meters across. |
| Novemeber 6th 2009 ASTEROID NEAR MISS: at 2132 UT, asteroid 2009 VA barely missed Earth when it flew just 14,000 km above the planet's surface. That's well inside the "Clarke Belt" of geosynchronous satellites. If it had hit, the 6 metre wide space rock would have disintegrated in the atmosphere as a spectacular fireball, causing no significant damage to the ground. 2009 VA was discovered just 15 hours before closest approach by astronomers working at the Catalina Sky Survey. |
NEO Links |
| For a complete list of recent NEO's CNEOS |
| Potential future Earth impact events that the CNEOS Sentry System has detected based on currently available observations |
Page redesigned 12-Mar-2017 - following JPL closing, data now from cneos







 Feed
Feed Scan with QR Code Reader
Scan with QR Code Reader mobi
mobi



