Earthquake Facts and Statistics
Plate Tectonics
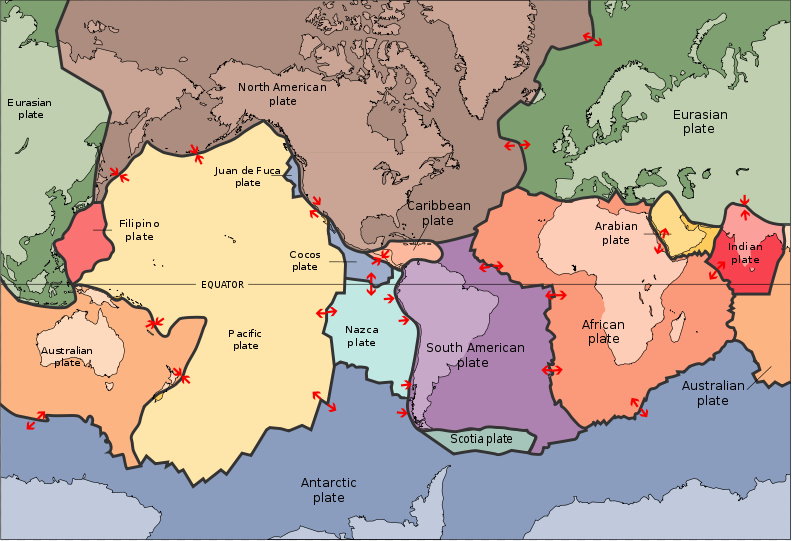
Plate Tectonics Map by USGS
There are six major plates, named for the continents embedded within them, such as the North American, African, and Antarctic plates and dozens of smaller, or minor, plates. The plates make up Earth's outer shell, called the lithosphere. Churning currents in the molten rocks below propel them along like a jumble of conveyor belts. The movement of the plates creates three types of tectonic boundaries: convergent, where plates move into one another; divergent, where plates move apart; and transform, where plates move sideways in relation to each other.
Convergent Boundaries
Where plates serving landmasses collide, the crust crumples and buckles into mountain ranges.
India and Asia crashed about 55 million years ago, slowly giving rise to the Himalaya
Divergent Boundaries
In the oceans, magma from deep in the Earth's mantle rises toward the surface and pushes apart two or more plates. Mountains and volcanoes rise along the seam
On land, giant troughs such as the Great Rift Valley in Africa form where plates are tugged apart.
Transform Boundaries
The San Andreas Fault in California is an example of a transform boundary, where two plates grind past each
other along what are called strike-slip faults
Check out the list of magnitude 8 and greater earthquakes since 1900, Here
March 2011, Japan's coastline may have shifted by as much as 4m (13ft) to the east following the 8.9 Magnitude earthquake on friday 11th, according to experts also the quake probably shifted Earth on its axis by about 6.5 inches (16.5cm) and caused the planet to rotate somewhat faster, shortening the length of the day by about 1.8 millionths of a second.
Earthquake Statistics
Number of Earthquakes Worldwide for 2000 - 2011
Located by the US Geological Survey National Earthquake Information Center
Last updated 15th March 2011| Magnitude | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8.0 to 9.9 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 7.0 to 7.9 | 14 | 15 | 13 | 14 | 14 | 10 | 9 | 14 | 12 | 16 | 21 | 11 |
| 6.0 to 6.9 | 146 | 121 | 127 | 140 | 141 | 140 | 142 | 178 | 168 | 144 | 151 | 128 |
Frequency of Occurrence of Earthquakes
| Magnitude | Average Annually |
|---|---|
| 8 and higher | 1 ¹ |
| 7 - 7.9 | 15 ¹ |
| 6 - 6.9 | 134 ² |
| 5 - 5.9 | 1319 ² |
| 4 - 4.9 | 13,000 (estimated) |
| 3 - 3.9 | 130,000 (estimated) |
| 2 - 2.9 | 1,300,000 (estimated) |
¹ Based on observations since 1900.
² Based on observations since 1990.







 Feed
Feed Scan with QR Code Reader
Scan with QR Code Reader mobi
mobi



